Liquidation
The liquidation mechanism plays a pivotal role in margin trading, exerting a direct influence on the health and prosperity of the market.
Monitor
Liquidations are being processed from Jungle smart contracts.
Monitoring encompasses several fundamental steps:
-
Gather fundamental parameters of the contract market, such as maintenance margin rate.
-
Retrieve the present positions held within the market.
-
Acquire mark price data (real-time from on-chain oracles).
-
Calculate if the held positions trigger liquidation.
-
If positive, liquidation will be processed through relevant contracts.
Executor
Liquidation execution:
-
Upon receipt of a liquidation request, an assessment is conducted to determine if the positions have indeed triggered liquidation.
-
If negative, a response is issued, indicating liquidation failure due to triggering conditions unmet.
-
If positive, an immediate verification of liquidity adequacy is carried out through the Router.
-
If positive, meaning that there is sufficient liquidity available, order will be executed via the Router.
-
If negative, the ADL Manager is employed to facilitate order-matching in a one-to-many manner to ensure the total liquidity matches the position.
-
Upon successful liquidation, relevant users will be notified (if email is binded)
-
Distribute rewards (real-time or cumulatively) to the liquidation initiators based on past records.
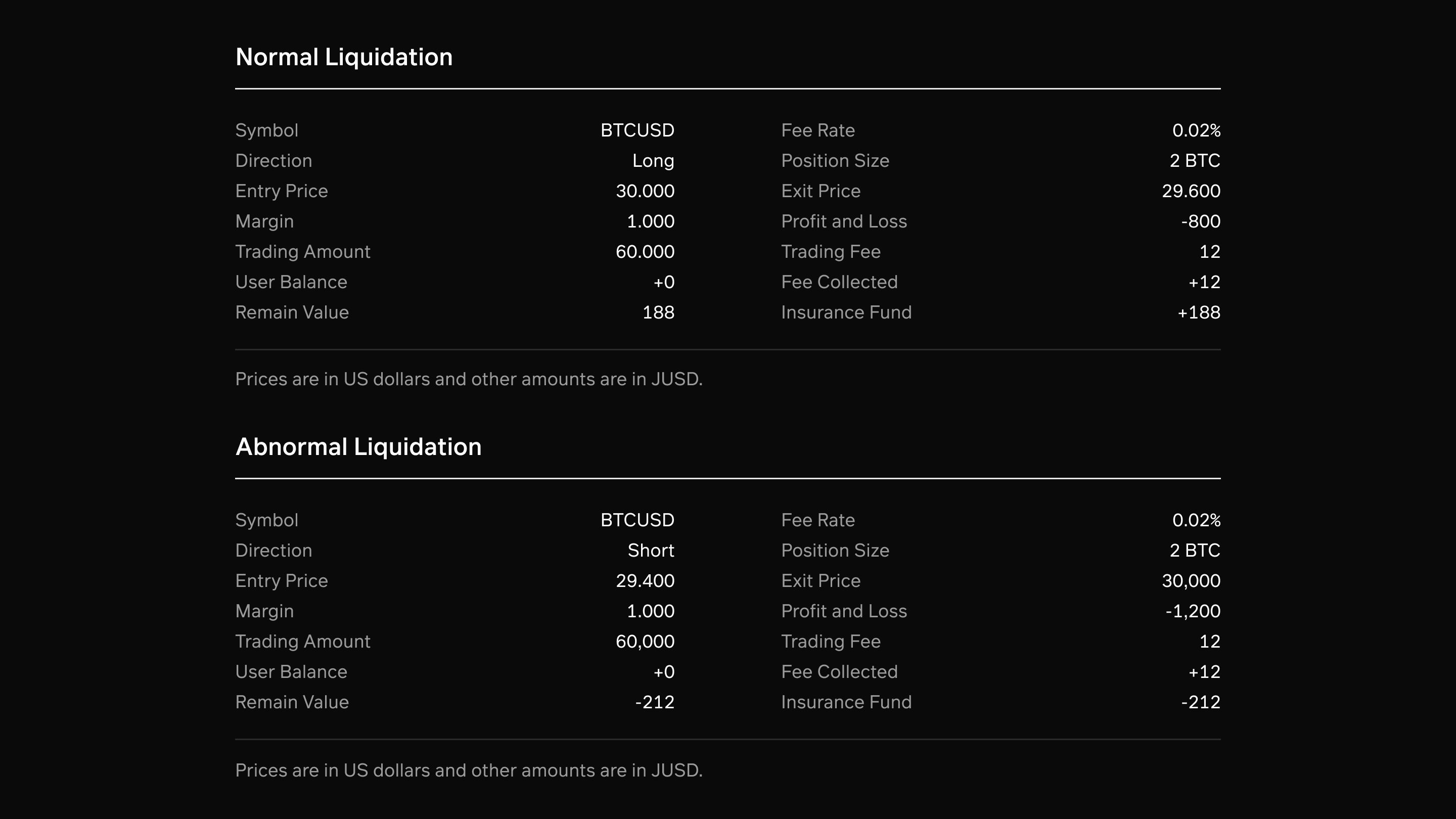
Abnormal Liquidation
Due to delayed liquidations or extreme price fluctuations within a short time period, abnormal liquidations may occur, resulting in positions being liquidated with Net Value. In this scenario, bad debt appears in the USDC ledger of opening positions, and corrective actions are taken:
-
Funds are injected from the Insurance Fund into the ledger.
-
The bad debt is eliminated (negative value adjusted to zero), and the user can resume normal trading.
-
When the funds in the Insurance Fund are insufficient to cover the bad debt, the mechanism below may be enforced
-
Proportional Splitting Mechanism: paid and shared proportionally amongst traders in the pool who have profited
To illustrate the difference between normal and abnormal liquidations, consider the following example: